At least 60% of earth surface are covered by snow, permanently or seasonally. Snow pack is not only a insulating layer but also directly affect soil moisture and soil freezing and thawing cycles strongly affect the C/N cycling of terrestrial ecosystem. There are many reports on this subjects. However, there are discrepancies in literature. These may resulted from different ecosystem types, methods and the time span of the controlled experiments.
Under the guidance of Prof JIN Changjie , a graduate student LI Weibin and co-workers, using Meta-analysis, probed into the effect of changes in snow-pack on C/N pool and its variations, discussed the advantage and short age of test methods and time span of the experiments. The results are shown in figure 1.
First, Nitrogen cycle of terrestrial ecosystem is more sensitive than Carbon cycle. Increase in snow-pack depth increases N content in leaf litter and soil, increases CO2 emission but decrease N2O emission from Soil and decreases soil CO2 pool. Forest ecosystem is less sensitive than other ecosystems in this context. Concerning methodology, the method of Snow-fence and Shelter is better than others in long-term experiment.
The results were published in Soil Biology an d Biochemistry (2016,100,51-58) entitled as Response of terrestrial nitrogen dynamics to snow cover change: A meta-analysis of experimental manipulation and in Soil Biology and Soil Biochemistry (2016,103,388-393) ,entitled as Response of terrestrial carbon dynamics to snow cover change: A meta-analysis of experimental manipulation (II).
The work was supported by CAS Pilot Strategic Project (XDB15010301) and NNSFC (NO 41375119, 31522010 ).
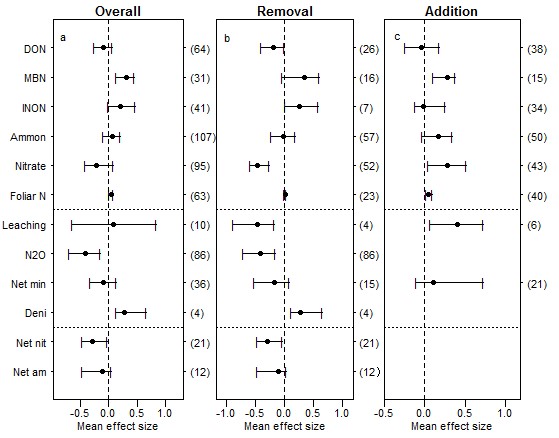
figure 1